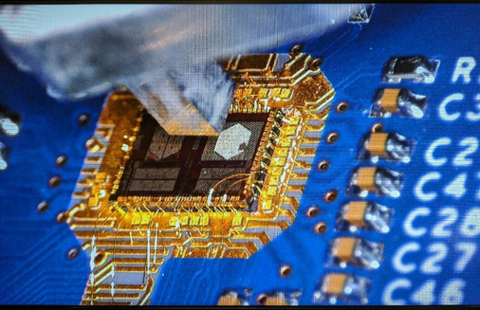
Avicena, headquartered in Sunnyvale, CA, has brought attention to the SuperComputing Conference 2023 in Denver, CO, by presenting what they claim to be the world’s smallest 1Tbps optical transceiver. This unveiling forms a part of Avicena’s LightBundle multi-Tbps chip-to-chip interconnect technology, a solution purported to bolster communication among processors, memory units, and sensors.
The technology’s development is primarily driven by the escalating demand for higher density, low-power interconnects, fueled by the exponential growth in AI applications like large language models such as ChatGPT. These applications require substantial computing power and rapid access to extensive memory resources.
Avicena’s microLED-based LightBundle technology aims to address these pressing requirements. In contrast to traditional solutions like Silicon Photonics (SiPh) or VCSELs, Avicena claims that their innovation offers a considerably smaller footprint, reduced power consumption, and decreased latency, potentially promising advancements in chip-to-chip communication.
Bardia Pezeshki, Avicena’s CEO, conveyed enthusiasm about the company’s patented microLED optical interface, highlighting its compact size, higher bandwidth density, and purported temperature tolerance of up to 150°C. These attributes are presented as advantageous features, particularly suitable for shorter-range interconnects.
The technology has garnered support from key investors, including Samsung Catalyst Fund, Cerberus Capital Management, Clear Ventures, and Micron Ventures, indicative of the industry’s interest and confidence in Avicena’s endeavors.
Industry experts, notably Marco Chisari from the Samsung Semiconductor Innovation Center, acknowledge the potential impact of Avicena’s LightBundle technology. Chisari emphasized its roadmap promising multi-Tbps capacity and purportedly superior power efficiency, envisioning potential enhancements in chip-to-chip and inter-rack performance.
While Avicena’s display at SC23 serves as a notable showcase of advancements in optical transceiver technology, its practical implementation and widespread adoption within the computing industry will ultimately determine its real-world efficacy and influence on the evolving landscape of high-performance computing.